Drug Trials Snapshots: QUVIVIQ
HOW TO USE THIS SNAPSHOT
The information provided in Snapshots highlights who participated in the clinical trials that supported the FDA approval of this drug, and whether there were differences among sex, race and age groups. The “MORE INFO” bar shows more detailed, technical content for each section. The Snapshot is intended as one tool for consumers to use when discussing the risks and benefits of the drugs.
LIMITATIONS OF THIS SNAPSHOT
Do not rely on Snapshots to make decisions regarding medical care. Always speak to your healthcare provider about the benefits and risks of a drug.
Snapshots are limited to the information available at the time of the original approval of the drug and do not provide information on who participated in clinical trials that supported later approvals for additional uses of the drug (if applicable). Refer to the QUVIVIQ Prescribing Information for all of the approved conditions of use of this drug (e.g., indication(s), population(s), dosing regimen(s), safety information).
QUVIVIQ (daridorexant)
cue-VIH-vick
Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd
Approval date: 01/07/2022
DRUG TRIALS SNAPSHOT SUMMARY:
What is the drug for?
QUVIVIQ is a prescription medicine that is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with insomnia, characterized by difficulties with sleep onset and/or sleep maintenance.
How is this drug used?
QUVIVIQ is a taken orally no more than once per night within 30 minutes of going to bed.
Who participated in the clinical trials?
The FDA approved QUVIVIQ based on evidence from two clinical studies [Study 1 (NCT03545191) and Study 2 (NCT03575104)] of 1,854 patients with chronic insomnia (sleep problems that have been happening most of the time for at least 3 months). The studies were conducted at 154 sites in 18 countries (Australia, Belgium, Bulgaria Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Republic of South Korea, Serbia, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, and the USA).
What are the benefits of this drug?
On average, patients who received QUVIVIQ fell asleep faster at bedtime, spent less time awake at night after first falling asleep, and felt they slept longer, compared to patients who received placebo.
What are the benefits of this drug (results of trials used to assess efficacy)?
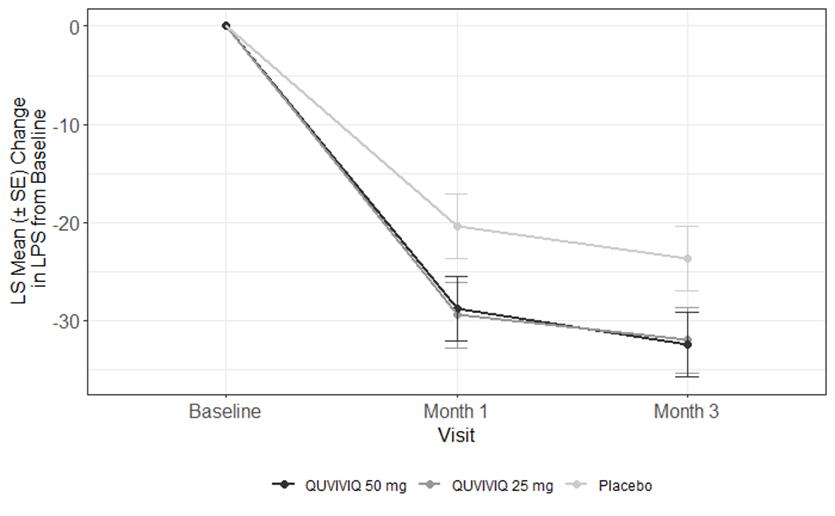
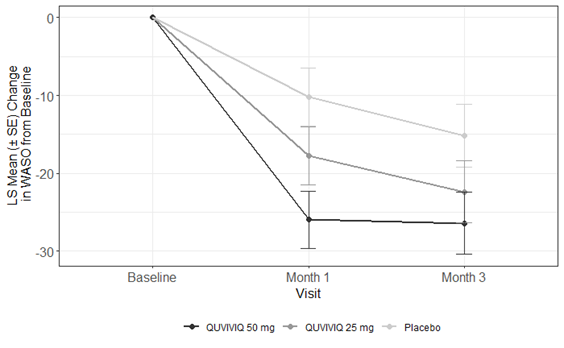
The figures below show the average changes in time to sleep onset (how long it takes to fall asleep), sleep maintenance (how much time is spent awake at night after first falling asleep), and subjective total sleep time (how long patients felt they slept in total) for the patients in Study 1. Sleep onset and sleep maintenance were measured in a sleep lab and subjective total sleep time was self-reported by patients. Results from Study 2 were similar.
Table 1. Primary and Secondary Efficacy Results for Change from Baseline in Sleep Onset, Sleep Maintenance, and Subjective Total Sleep Time at Month 1 and Month 3 in Patients with Insomnia (Study 1)
|
Treatment group/ dose (N) |
Baseline |
Month 1 |
Month 3 |
||||
|
|
|
Change from baseline |
Difference to placebo |
|
Change from baseline |
Difference to placebo |
|
|
mean (SD) |
mean (SD) |
LSM (95%CL) |
LSM (95%CL) |
mean (SD) |
LSM (95%CL) |
LSM |
|
|
WASO (wake after sleep onset, min): sleep maintenance, assessed by PSG |
|||||||
|
50 mg (310) |
95 (38) |
65 (35) |
-29 [-33, -25] |
-23* [-28, -18] |
65 (39) |
-29 [-33, -25] |
-18* [-24, -13] |
|
25 mg (310) |
98 (39) |
77 (42) |
-18 [-22, -15] |
-12* [-17, -7] |
73 (40) |
-23 [-27, -19] |
-12* [-17, -6] |
|
placebo (310) |
103 (41) |
92 (42) |
-6 [-10, -2] |
|
87 (43) |
-11 [-15, -7] |
|
|
LPS (latency to persistent sleep, min): sleep onset, assessed by PSG |
|||||||
|
50 mg (310) |
64 (37) |
34 (27) |
-31 [-35, -28] |
-11* [-16, -7] |
30 (23) |
-35 [-38, -31] |
-12* [-16, -7] |
|
25 mg (310) |
67 (39) |
38 (32) |
-28 [-32, -25] |
-8* [-13, -4] |
36 (34) |
-31 [-34, -27] |
-8* [-12, -3] |
|
placebo (310) |
67 (40) |
46 (36) |
-20 [-23, -17] |
|
43 (34) |
-23 [-26, -20] |
|
|
sTST (subjective total sleep time, min): patient-reported |
|||||||
|
50 mg (310) |
313 (58) |
358 (74) |
44 [38, 49] |
22* [14, 30] |
372 (79) |
58 [51, 64] |
20* [11, 29] |
|
25 mg (310) |
310 (60) |
345 (66) |
34 [29, 40] |
13* [5, 20] |
358 (72) |
48 [41, 54] |
10* [1, 19] |
|
placebo (310) |
316 (53) |
338 (65) |
22 [16, 27] |
|
354 (73) |
38 [31, 44] |
|
* doses that were statistically significantly superior (p < 0.05) to placebo after controlling for multiple comparisons. CL = confidence limit; LPS = latency to persistent sleep; LSM = least squares mean; PSG = polysomnography; SD = standard deviation; sTST = subjective total sleep time; WASO = wake after sleep onset.
Adapted from FDA review
Table 2. Primary and Secondary Efficacy Results for Change from Baseline in Sleep Onset, Sleep Maintenance, and Subjective Total Sleep Time at Month 1 and Month 3 in Patients with Insomnia (Study 2)
|
Treatment group/ dose (N) |
Baseline |
Month 1 |
Month 3 |
||||
|
|
|
Change from baseline
|
Difference to placebo |
|
Change from baseline |
Difference to placebo |
|
|
mean (SD) |
mean (SD) |
LSM (95%CL) |
LSM (95%CL) |
mean (SD) |
LSM (95%CL) |
LSM (95%CL) |
|
|
WASO (wake after sleep onset, min): sleep maintenance, assessed by PSG |
|||||||
|
25 mg (309) |
106 (49) |
80 (44) |
-24 [-28, -20] |
-12* [-18, -6] |
80 (49) |
-24 [-29, -19] |
-10* [-17, -4] |
|
placebo (308) |
108 (49) |
93 (50) |
-13 [-17, -8] |
|
91 (47) |
-14 [-19, -9] |
|
|
LPS (latency to persistent sleep, min): sleep onset, assessed by PSG |
|||||||
|
25 mg (309) |
69 (41) |
42 (39) |
-26 [-31, -22] |
-6 [-12, -1] |
39 (37) |
-29 [-33, -24] |
-9 [-15, -3] |
|
placebo (308) |
72 (46) |
50 (40) |
-20 [-24, -16] |
|
49 (46) |
-20 [-24, -15] |
|
|
sTST (subjective total sleep time, min): patient-reported |
|||||||
|
25 mg (309) |
308 (53) |
353 (67) |
44 [38, 49] |
16* [8, 24] |
365 (70) |
56 [50, 63] |
19* [10, 28] |
|
placebo (308) |
308 (52) |
336 (63) |
28 [22, 33] |
|
347 (65) |
37 [31, 43] |
|
* doses that were statistically significantly superior (p < 0.05) to placebo after controlling for multiple comparisons.
Adapted from FDA review
Figure 1. Change in Time to Fall Asleep (LPS) by Month
Adapted from FDA review
Figure 2. Change in Time Awake After First Falling Asleep (WASO) by Month
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race and age?
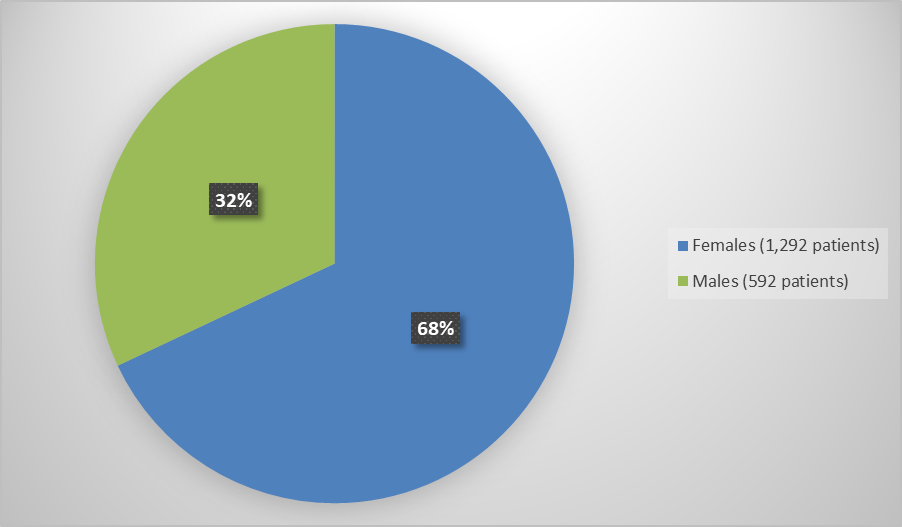
- Sex: QUVIVIQ worked similarly in males and females
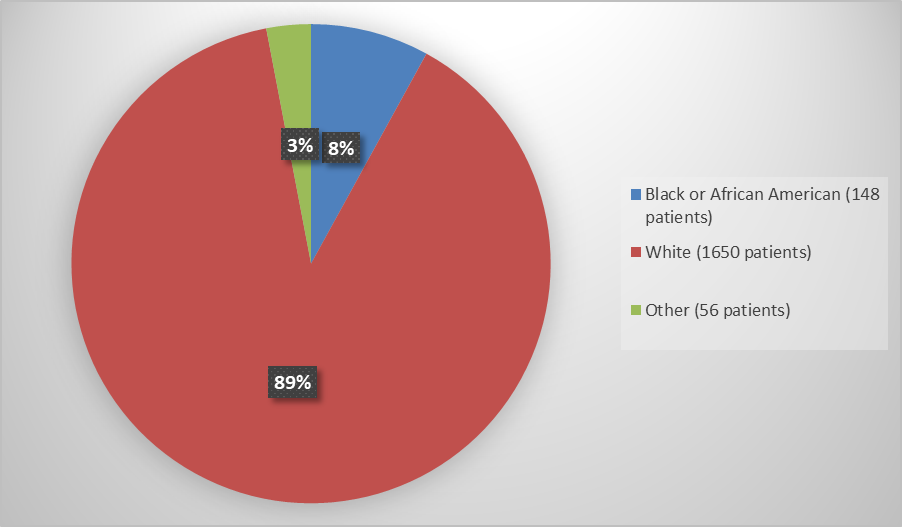
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in how QUVIVIQ worked among races could not be determined.
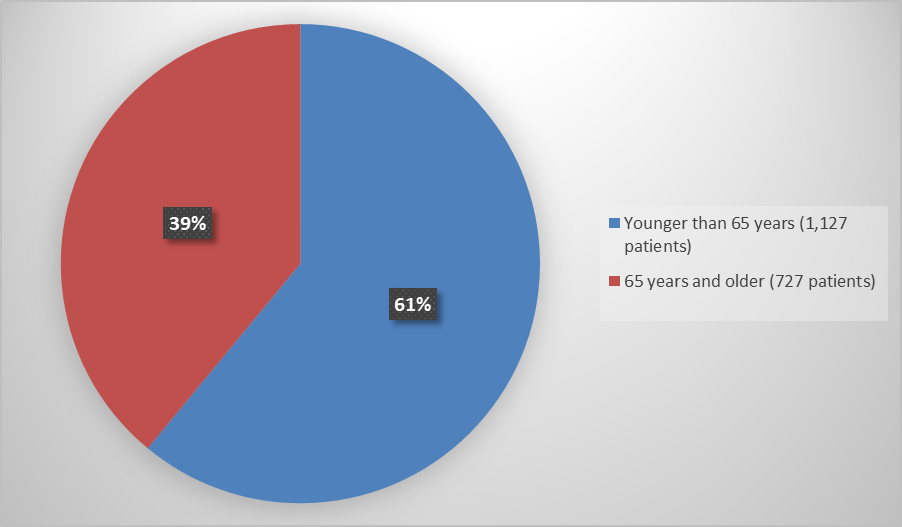
- Age: QUVIVIQ worked similarly in patients younger and older than 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in how well the drug worked in clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The table below summarizes the demographics for the efficacy population.
Table 5 Demographic Information for the Efficacy Population
|
Demographic Parameters |
Study 1 (N=930) |
Study 2 (N=924) |
Total (N=1854) |
|
Sex, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
Female |
624 (67) |
638 (69) |
1262 (68) |
|
Male |
306 (33) |
286 (31) |
592 (32) |
|
Race, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
White |
839 (90) |
811 (88) |
1650 (89) |
|
Black or African American |
77 (8) |
71 (8) |
148 (8) |
|
Other |
14 (2) |
42 (4) |
56 (3) |
|
Age Group, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
<65 years |
566 (61) |
561 (61) |
1127 (61) |
|
>=65 years |
364 (39) |
363 (39) |
727 (39) |
|
Ethnicity, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
Hispanic or Latino |
146 (16) |
47 (5) |
193 (10) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
784 (84) |
877 (95) |
1661 (90) |
Sponsor generated table
What are the possible side effects?
The most common side effects of QUVIVIQ are headache and sleepiness.
Sleep medicine, such as QUVIVIQ, may cause serious side effects including:
- Decreased awareness and alertness.
- Worsening depression and suicidal thoughts.
- Temporary inability to move or talk while going to sleep or waking up (sleep paralysis) for up to several minutes.
- Hallucinations while going to sleep or waking up.
- Complex sleep behaviors (e.g., sleep-walking, sleep-driving).
What are the possible side effects (results of trials used to assess safety)?
The table below summarizes the adverse reactions that occurred during the 3-month placebo-controlled study.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 2% of QUVIVIQ-treated Patients and Greater than in Placebo-treated Patients in a 3-Month Placebo-Controlled Study (Study 1)
|
|
QUVIVIQ 25 mg (N=310) % |
QUVIVIQ 50 mg (N=308) % |
Placebo
(N=309) % |
|
Headache |
6 |
7 |
5 |
|
Somnolence or fatigue |
6 |
5 |
4 |
|
Dizziness |
2 |
3 |
2 |
|
Nausea |
0 |
3 |
2 |
Adapted from FDA review
Were there any differences in side effects among sex, race and age?
- Sex: The occurrence of side effects was similar in males and females
- Race: The number of patients of races other than White was small; therefore, differences in the occurrence of side effects could not be determined.
- Age: The occurrence of somnolence or fatigue side effects were greater in patients above 65 years of age.
Were there any differences in side effects of the clinical trials among sex, race, and age groups?
The tables below summarize the adverse events of somnolence or fatigue by age subgroups. The table includes all patients who received placebo or QUVIVIQ in Study 1 over a three-month period.
Table 4. Somnolence or fatigue side effects by age (Study 1)
|
|
QUVIVIQ 25 mg % |
QUVIVIQ 50 mg % |
Placebo % |
|
|
Sex |
Female |
6 |
6 |
3 |
|
|
Male |
7 |
3 |
4 |
|
Race |
Black or African American |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
|
White |
7 |
5 |
4 |
|
Age (years) |
<65 |
5 |
4 |
4 |
|
|
>=65 |
8 |
5 |
2 |
Sponsor generated table
Presented below is the population that provided data for the assessment of QUVIVIQ’s benefit (efficacy population) for Studies 1 and 2 combined. The demographics were similar for each individual study.
Figure 5. Demographics by Race
Adapted from Sponsor generated table
Figure 6. Demographics by Age
WHO WAS IN THE CLINICAL TRIALS?
Who participated in the trials?
Who participated in the trials?
The table below summarizes the demographics for the efficacy population.
Table 5 Demographic Information for the Efficacy Population
|
Demographic Parameters |
Study 1 (N=930) |
Study 2 (N=924) |
Total (N=1854) |
|
Sex, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
Female |
624 (67) |
638 (69) |
1262 (68) |
|
Male |
306 (33) |
286 (31) |
592 (32) |
|
Race, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
White |
839 (90) |
811 (88) |
1650 (89) |
|
Black or African American |
77 (8) |
71 (8) |
148 (8) |
|
Other |
14 (2) |
42 (4) |
56 (3) |
|
Age Group, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
<65 years |
566 (61) |
561 (61) |
1127 (61) |
|
>=65 years |
364 (39) |
363 (39) |
727 (39) |
|
Ethnicity, number of patients (%) |
|
|
|
|
Hispanic or Latino |
146 (16) |
47 (5) |
193 (10) |
|
Not Hispanic or Latino |
784 (84) |
877 (95) |
1661 (90) |
Sponsor generated table
How were the trials designed?
QUVIVIQ was evaluated in two clinical studies for efficacy (how well the drug works) and safety (what the side effects are). The patients in the studies had chronic insomnia (sleep problems that have been happening most of the time for at least 3 months).
In Study 1, adult patients (18 years old and above) were given 25 mg QUVIVIQ pills, 50 mg QUVIVIQ pills, or placebo pills (identical-appearing pill with no drug in it) to take every night for 3 months. In Study 2, adult patients (18 years old and above) were given 10 mg QUVIVIQ pills, 25 mg QUVIVIQ pills, or placebo pills (identical-appearing pill with no drug in it) to take every night for 3 months. The 10 mg dose is not an approved dose. It did not work better than placebo.
In both studies, the pills looked identical so neither the patients nor the healthcare providers knew which pill was being given. Sleep was measured using polysomnography (PSG), an overnight test done in a sleep laboratory, and by using a sleep diary where patients wrote how long they felt they slept each night. The benefit of QUVIVIQ was evaluated by comparing the QUVIVIQ and placebo groups’ changes in sleep (based on PSG and the sleep diary).
How were the trials designed?
The efficacy and safety of QUVIVIQ were assessed in adult and elderly patients who met DSM-5 criteria for insomnia disorder in two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies.
In Study 1, patients were randomly chosen to get either QUVIVIQ 25 mg, QUVIVIQ 50 mg, or placebo once nightly for 3 months. In Study 2, patients were randomly chosen to get either QUVIVIQ 10 mg, QUVIVIQ 25 mg, or placebo once nightly for 3 months. (The 10 mg dose is not an approved dose.) All the patients who got the same treatment (for example, all the patients who got the placebo pill) is called a treatment group.
In both studies, how well the drug worked was tested by comparing how much the sleep of the average patient in each treatment group changed from baseline (before getting treatment in the study) to Month 1 and Month 3. Sleep was checked by polysomnography (PSG) in a sleep laboratory at baseline, after 1 month of treatment and after 3 months of treatment. Polysomnography uses recordings of a person’s brain waves, oxygen levels, heartbeat, breathing, and eye and leg movements. An expert reads these recordings to see when they were awake or asleep. It was used to measure how long it took patients to fall asleep (called “Latency to Persistent Sleep”) and how much time they spent awake after first falling asleep (called “Wake After Sleep Onset”). To support the evidence from polysomnography, every morning, at home, patients also reported in a sleep diary how long they felt they slept the night before (called “subjective Total Sleep Time”).
GLOSSARY
CLINICAL TRIAL: Voluntary research studies conducted in people and designed to answer specific questions about the safety or effectiveness of drugs, vaccines, other therapies, or new ways of using existing treatments.
COMPARATOR: A previously available treatment or placebo used in clinical trials that is compared to the actual drug being tested.
EFFICACY: How well the drug achieves the desired response when it is taken as described in a controlled clinical setting, such as during a clinical trial.
PLACEBO: An inactive substance or “sugar pill” that looks the same as, and is given the same way as, an active drug or treatment being tested. The effects of the active drug or treatment are compared to the effects of the placebo.
SUBGROUP: A subset of the population studied in a clinical trial. Demographic subsets include sex, race, and age groups.