amino acids
Biomedical Research Leads Science’s 2021 Breakthroughs
Posted on by Lawrence Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D.
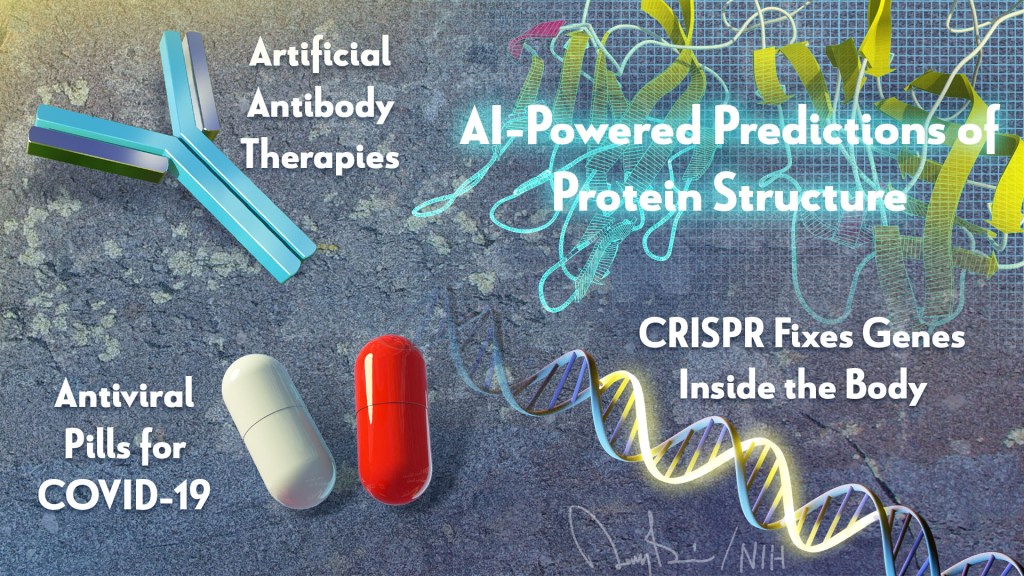
Hi everyone, I’m Larry Tabak. I’ve served as NIH’s Principal Deputy Director for over 11 years, and I will be the acting NIH director until a new permanent director is named. In my new role, my day-to-day responsibilities will certainly increase, but I promise to carve out time to blog about some of the latest research progress on COVID-19 and any other areas of science that catch my eye.
I’ve also invited the directors of NIH’s Institutes and Centers (ICs) to join me in the blogosphere and write about some of the cool science in their research portfolios. I will publish a couple of posts to start, then turn the blog over to our first IC director. From there, I envision alternating between posts from me and from various IC directors. That way, we’ll cover a broad array of NIH science and the tremendous opportunities now being pursued in biomedical research.
Since I’m up first, let’s start where the NIH Director’s Blog usually begins each year: by taking a look back at Science’s Breakthroughs of 2021. The breakthroughs were formally announced in December near the height of the holiday bustle. In case you missed the announcement, the biomedical sciences accounted for six of the journal Science’s 10 breakthroughs. Here, I’ll focus on four biomedical breakthroughs, the ones that NIH has played some role in advancing, starting with Science’s editorial and People’s Choice top-prize winner:
Breakthrough of the Year: AI-Powered Predictions of Protein Structure
The biochemist Christian Anfinsen, who had a distinguished career at NIH, shared the 1972 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, for work suggesting that the biochemical interactions among the amino acid building blocks of proteins were responsible for pulling them into the final shapes that are essential to their functions. In his Nobel acceptance speech, Anfinsen also made a bold prediction: one day it would be possible to determine the three-dimensional structure of any protein based on its amino acid sequence alone. Now, with advances in applying artificial intelligence to solve biological problems—Anfinsen’s bold prediction has been realized.
But getting there wasn’t easy. Every two years since 1994, research teams from around the world have gathered to compete against each other in developing computational methods for predicting protein structures from sequences alone. A score of 90 or above means that a predicted structure is extremely close to what’s known from more time-consuming work in the lab. In the early days, teams more often finished under 60.
In 2020, a London-based company called DeepMind made a leap with their entry called AlphaFold. Their deep learning approach—which took advantage of 170,000 proteins with known structures—most often scored above 90, meaning it could solve most protein structures about as well as more time-consuming and costly experimental protein-mapping techniques. (AlphaFold was one of Science’s runner-up breakthroughs last year.)
This year, the NIH-funded lab of David Baker and Minkyung Baek, University of Washington, Seattle, Institute for Protein Design, published that their artificial intelligence approach, dubbed RoseTTAFold, could accurately predict 3D protein structures from amino acid sequences with only a fraction of the computational processing power and time that AlphaFold required [1]. They immediately applied it to solve hundreds of new protein structures, including many poorly known human proteins with important implications for human health.
The DeepMind and RoseTTAFold scientists continue to solve more and more proteins [1,2], both alone and in complex with other proteins. The code is now freely available for use by researchers anywhere in the world. In one timely example, AlphaFold helped to predict the structural changes in spike proteins of SARS-CoV-2 variants Delta and Omicron [3]. This ability to predict protein structures, first envisioned all those years ago, now promises to speed fundamental new discoveries and the development of new ways to treat and prevent any number of diseases, making it this year’s Breakthrough of the Year.
Anti-Viral Pills for COVID-19
The development of the first vaccines to protect against COVID-19 topped Science’s 2020 breakthroughs. This year, we’ve also seen important progress in treating COVID-19, including the development of anti-viral pills.
First, there was the announcement in October of interim data from Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, and Ridgeback Biotherapeutics, Miami, FL, of a significant reduction in hospitalizations for those taking the anti-viral drug molnupiravir [4] (originally developed with an NIH grant to Emory University, Atlanta). Soon after came reports of a Pfizer anti-viral pill that might target SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19, even more effectively. Trial results show that, when taken within three days of developing COVID-19 symptoms, the pill reduced the risk of hospitalization or death in adults at high risk of progressing to severe illness by 89 percent [5].
On December 22, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Pfizer’s Paxlovid to treat mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in people age 12 and up at high risk for progressing to severe illness, making it the first available pill to treat COVID-19 [6]. The following day, the FDA granted an EUA for Merck’s molnupiravir to treat mild-to-moderate COVID-19 in unvaccinated, high-risk adults for whom other treatment options aren’t accessible or recommended, based on a final analysis showing a 30 percent reduction in hospitalization or death [7].
Additional promising anti-viral pills for COVID-19 are currently in development. For example, a recent NIH-funded preclinical study suggests that a drug related to molnupiravir, known as 4’-fluorouridine, might serve as a broad spectrum anti-viral with potential to treat infections with SARS-CoV-2 as well as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) [8].
Artificial Antibody Therapies
Before anti-viral pills came on the scene, there’d been progress in treating COVID-19, including the development of monoclonal antibody infusions. Three monoclonal antibodies now have received an EUA for treating mild-to-moderate COVID-19, though not all are effective against the Omicron variant [9]. This is also an area in which NIH’s Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines (ACTIV) public-private partnership has made big contributions.
Monoclonal antibodies are artificially produced versions of the most powerful antibodies found in animal or human immune systems, made in large quantities for therapeutic use in the lab. Until recently, this approach had primarily been put to work in the fight against conditions including cancer, asthma, and autoimmune diseases. That changed in 2021 with success using monoclonal antibodies against infections with SARS-CoV-2 as well as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and other infectious diseases. This earned them a prominent spot among Science’s breakthroughs of 2021.
Monoclonal antibodies delivered via intravenous infusions continue to play an important role in saving lives during the pandemic. But, there’s still room for improvement, including new formulations highlighted on the blog last year that might be much easier to deliver.
CRISPR Fixes Genes Inside the Body
One of the most promising areas of research in recent years has been gene editing, including CRISPR/Cas9, for fixing misspellings in genes to treat or even cure many conditions. This year has certainly been no exception.
CRISPR is a highly precise gene-editing system that uses guide RNA molecules to direct a scissor-like Cas9 enzyme to just the right spot in the genome to cut out or correct disease-causing misspellings. Science highlights a small study reported in The New England Journal of Medicine by researchers at Intellia Therapeutics, Cambridge, MA, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Tarrytown, NY, in which six people with hereditary transthyretin (TTR) amyloidosis, a condition in which TTR proteins build up and damage the heart and nerves, received an infusion of guide RNA and CRISPR RNA encased in tiny balls of fat [10]. The goal was for the liver to take them up, allowing Cas9 to cut and disable the TTR gene. Four weeks later, blood levels of TTR had dropped by at least half.
In another study not yet published, researchers at Editas Medicine, Cambridge, MA, injected a benign virus carrying a CRISPR gene-editing system into the eyes of six people with an inherited vision disorder called Leber congenital amaurosis 10. The goal was to remove extra DNA responsible for disrupting a critical gene expressed in the eye. A few months later, two of the six patients could sense more light, enabling one of them to navigate a dimly lit obstacle course [11]. This work builds on earlier gene transfer studies begun more than a decade ago at NIH’s National Eye Institute.
Last year, in a research collaboration that included former NIH Director Francis Collins’s lab at the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), we also saw encouraging early evidence in mice that another type of gene editing, called DNA base editing, might one day correct Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome, a rare genetic condition that causes rapid premature aging. Preclinical work has even suggested that gene-editing tools might help deliver long-lasting pain relief. The technology keeps getting better, too. This isn’t the first time that gene-editing advances have landed on Science’s annual Breakthrough of the Year list, and it surely won’t be the last.
The year 2021 was a difficult one as the pandemic continued in the U.S. and across the globe, taking far too many lives far too soon. But through it all, science has been relentless in seeking and finding life-saving answers, from the rapid development of highly effective COVID-19 vaccines to the breakthroughs highlighted above.
As this list also attests, the search for answers has progressed impressively in other research areas during these difficult times. These groundbreaking discoveries are something in which we can all take pride—even as they encourage us to look forward to even bigger breakthroughs in 2022. Happy New Year!
References:
[1] Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Baek M, DiMaio F, Anishchenko I, Dauparas J, Grishin NV, Adams PD, Read RJ, Baker D., et al. Science. 2021 Jul 15:eabj8754.
[2] Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Senior AW, Kavukcuoglu K, Kohli P, Hassabis D. et al. Nature. 2021 Jul 15.
[3] Structural insights of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein from Delta and Omicron variants. Sadek A, Zaha D, Ahmed MS. preprint bioRxiv. 2021 Dec 9.
[5] Pfizer’s novel COVID-19 oral antiviral treatment candidate reduced risk of hospitalization or death by 89% in interim analysis of phase 2/3 EPIC-HR Study. Pfizer. 5 November 52021.
[6] Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA authorizes first oral antiviral for treatment of COVID-19. Food and Drug Administration. 22 Dec 2021.
[7] Coronavirus (COVID-19) Update: FDA authorizes additional oral antiviral for treatment of COVID-19 in certain adults. Food and Drug Administration. 23 Dec 2021.
[8] 4′-Fluorouridine is an oral antiviral that blocks respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-CoV-2 replication. Sourimant J, Lieber CM, Aggarwal M, Cox RM, Wolf JD, Yoon JJ, Toots M, Ye C, Sticher Z, Kolykhalov AA, Martinez-Sobrido L, Bluemling GR, Natchus MG, Painter GR, Plemper RK. Science. 2021 Dec 2.
[9] Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies. NIH COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines. 16 Dec 2021.
[10] CRISPR-Cas9 in vivo gene editing for transthyretin amyloidosis. Gillmore JD, Gane E, Taubel J, Kao J, Fontana M, Maitland ML, Seitzer J, O’Connell D, Walsh KR, Wood K, Phillips J, Xu Y, Amaral A, Boyd AP, Cehelsky JE, McKee MD, Schiermeier A, Harari O, Murphy A, Kyratsous CA, Zambrowicz B, Soltys R, Gutstein DE, Leonard J, Sepp-Lorenzino L, Lebwohl D. N Engl J Med. 2021 Aug 5;385(6):493-502.
[11] Editas Medicine announces positive initial clinical data from ongoing phase 1/2 BRILLIANCE clinical trial of EDIT-101 For LCA10. Editas Medicine. 29 Sept 2021.
Links:
Structural Biology (National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH)
The Structures of Life (NIGMS)
COVID-19 Research (NIH)
2021 Science Breakthrough of the Year (American Association for the Advancement of Science, Washington, D.C)
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Posted In: News
Tags: 4'-fluorouridine, Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines, ACTIV, AI, AlphaFold, amino acids, artificial antibodies, artificial intelligence, biochemistry, Christian Anfinsen, Chronic Pain, computational biology, coronavirus, COVID pill, COVID-19, CRISPR, CRISPR/Cas9, DeepMind, Delta variant, Editas Medicine, EUA, gene editing, hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis, Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome, Intellia Therapeutics, Leber congenital amaurosis, Merck, molnupiravir, monoclonal antibodies, Omicron variant, pandemic, Pfizer, progeria, protein structure, rare disease, Regeneron, RoseTTAFold, SARS-CoV-2, Science Breakthrough of the Year, Science Breakthroughs of 2021, structural biology
Artificial Intelligence Accurately Predicts Protein Folding
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Proteins are the workhorses of the cell. Mapping the precise shapes of the most important of these workhorses helps to unlock their life-supporting functions or, in the case of disease, potential for dysfunction. While the amino acid sequence of a protein provides the basis for its 3D structure, deducing the atom-by-atom map from principles of quantum mechanics has been beyond the ability of computer programs—until now.
In a recent study in the journal Science, researchers reported they have developed artificial intelligence approaches for predicting the three-dimensional structure of proteins in record time, based solely on their one-dimensional amino acid sequences [1]. This groundbreaking approach will not only aid researchers in the lab, but guide drug developers in coming up with safer and more effective ways to treat and prevent disease.
This new NIH-supported advance is now freely available to scientists around the world. In fact, it has already helped to solve especially challenging protein structures in cases where experimental data were lacking and other modeling methods hadn’t been enough to get a final answer. It also can now provide key structural information about proteins for which more time-consuming and costly imaging data are not yet available.
The new work comes from a group led by David Baker and Minkyung Baek, University of Washington, Seattle, Institute for Protein Design. Over the course of the pandemic, Baker’s team has been working hard to design promising COVID-19 therapeutics. They’ve also been working to design proteins that might offer promising new ways to treat cancer and other conditions. As part of this effort, they’ve developed new computational approaches for determining precisely how a chain of amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins, will fold up in space to form a finished protein.
But the ability to predict a protein’s precise structure or shape from its sequence alone had proven to be a difficult problem to solve despite decades of effort. In search of a solution, research teams from around the world have come together every two years since 1994 at the Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP) meetings. At these gatherings, teams compete against each other with the goal of developing computational methods and software capable of predicting any of nature’s 200 million or more protein structures from sequences alone with the greatest accuracy.
Last year, a London-based company called DeepMind shook up the structural biology world with their entry into CASP called AlphaFold. (AlphaFold was one of Science’s 2020 Breakthroughs of the Year.) They showed that their artificial intelligence approach—which took advantage of the 170,000 proteins with known structures in a reiterative process called deep learning—could predict protein structure with amazing accuracy. In fact, it could predict most protein structures almost as accurately as other high-resolution protein mapping techniques, including today’s go-to strategies of X-ray crystallography and cryo-EM.
The DeepMind performance showed what was possible, but because the advances were made by a world-leading deep learning company, the details on how it worked weren’t made publicly available at the time. The findings left Baker, Baek, and others eager to learn more and to see if they could replicate the impressive predictive ability of AlphaFold outside of such a well-resourced company.
In the new work, Baker and Baek’s team has made stunning progress—using only a fraction of the computational processing power and time required by AlphaFold. The new software, called RoseTTAFold, also relies on a deep learning approach. In deep learning, computers look for patterns in large collections of data. As they begin to recognize complex relationships, some connections in the network are strengthened while others are weakened. The finished network is typically composed of multiple information-processing layers, which operate on the data to return a result—in this case, a protein structure.
Given the complexity of the problem, instead of using a single neural network, RoseTTAFold relies on three. The three-track neural network integrates and simultaneously processes one-dimensional protein sequence information, two-dimensional information about the distance between amino acids, and three-dimensional atomic structure all at once. Information from these separate tracks flows back and forth to generate accurate models of proteins rapidly from sequence information alone, including structures in complex with other proteins.
As soon as the researchers had what they thought was a reasonable working approach to solve protein structures, they began sharing it with their structural biologist colleagues. In many cases, it became immediately clear that RoseTTAFold worked remarkably well. What’s more, it has been put to work to solve challenging structural biology problems that had vexed scientists for many years with earlier methods.
RoseTTAFold already has solved hundreds of new protein structures, many of which represent poorly understood human proteins. The 3D rendering of a complex showing a human protein called interleukin-12 in complex with its receptor (above image) is just one example. The researchers have generated other structures directly relevant to human health, including some that are related to lipid metabolism, inflammatory conditions, and cancer. The program is now available on the web and has been downloaded by dozens of research teams around the world.
Cryo-EM and other experimental mapping methods will remain essential to solve protein structures in the lab. But with the artificial intelligence advances demonstrated by RoseTTAFold and AlphaFold, which has now also been released in an open-source version and reported in the journal Nature [2], researchers now can make the critical protein structure predictions at their desktops. This newfound ability will be a boon to basic science studies and has great potential to speed life-saving therapeutic advances.
References:
[1] Accurate prediction of protein structures and interactions using a three-track neural network. Baek M, DiMaio F, Anishchenko I, Dauparas J, Grishin NV, Adams PD, Read RJ, Baker D., et al. Science. 2021 Jul 15:eabj8754.
[2] Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Jumper J, Evans R, Pritzel A, Green T, Senior AW, Kavukcuoglu K, Kohli P, Hassabis D. et al. Nature. 2021 Jul 15.
Links:
Structural Biology (National Institute of General Medical Sciences/NIH)
The Structures of Life (NIGMS)
Baker Lab (University of Washington, Seattle)
CASP 14 (University of California, Davis)
NIH Support: National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases; National Institute of General Medical Sciences
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Posted In: News
Tags: AI, AlphaFold, amino acids, artificial intelligence, basic science, cancer, computer learning, computer simulation, Critical Assessment of Structure, cryo-EM, deep learning, DeepMind, drug development, inflammatory disease, interleukin-12, lipid metabolism, protein, protein design, protein folding, quantum mechanics, RoseTTAFold, structural biology, x-ray crystallography
Adding Letters to the DNA Alphabet
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit: William B. Kiosses
The recipes for life, going back billions of years to the earliest single-celled organisms, are encoded in a DNA alphabet of just four letters. But is four as high as the DNA code can go? Or, as researchers have long wondered, is it chemically and biologically possible to expand the DNA code by a couple of letters?
A team of NIH-funded researchers is now answering these provocative questions. The researchers recently engineered a semi-synthetic bacterium containing DNA with six letters, including two extra nucleotides [1, 2]. Now, in a report published in Nature, they’ve taken the next critical step [3]. They show that bacteria, like those in the photo, are not only capable of reliably passing on to the next generation a DNA code of six letters, they can use that expanded genetic information to produce novel proteins unlike any found in nature.
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Posted In: Health, Science, technology
Tags: amino acids, bacteria, bioengineering, codon, DNA, DNA alphabet, DNA code, E. coli, expanded DNA code, genetic code, green fluorescent protein, nucleotides, protein, protein therapeutics, transfer RNA
The Beauty of Recycling
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Novel proteasome regulation image by Sigi Benjamin-Hong, Strang Laboratory of Apoptosis and Cancer Biology.
All cells recycle. Here, we see actin filaments (red) direct unwanted (malformed, damaged, or toxic) proteins to proteasomes (green). In these barrel-shaped compartments, proteins are chopped up into their basic building blocks, called amino acids, and recycled to make new healthy proteins.
Share this:
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Tumblr (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Posted In: Science
Tags: actin filaments, amino acids, apoptosis, bortezomib, cell recycling, cells, proteasome inhibitors, proteasomes, proteins, Velcade®
