hippocampus
Distinctive Brain ‘Subnetwork’ Tied to Feeling Blue
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit: :iStock/kieferpix
Experiencing a range of emotions is a normal part of human life, but much remains to be discovered about the neuroscience of mood. In a step toward unraveling some of those biological mysteries, researchers recently identified a distinctive pattern of brain activity associated with worsening mood, particularly among people who tend to be anxious.
In the new study, researchers studied 21 people who were hospitalized as part of preparation for epilepsy surgery, and took continuous recordings of the brain’s electrical activity for seven to 10 days. During that same period, the volunteers also kept track of their moods. In 13 of the participants, low mood turned out to be associated with stronger activity in a “subnetwork” that involved crosstalk between the brain’s amygdala, which mediates fear and other emotions, and the hippocampus, which aids in memory.
Study Suggests Light Exercise Helps Memory
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit: iStock/Wavebreakmedia
How much exercise does it take to boost your memory skills? Possibly a lot less than you’d think, according to the results of a new study that examined the impact of light exercise on memory.
In their study of 36 healthy young adults, researchers found surprisingly immediate improvements in memory after just 10 minutes of low-intensity pedaling on a stationary bike [1]. Further testing by the international research team reported that the quick, light workout—which they liken in intensity to a short yoga or tai chi session—was associated with heightened activity in the brain’s hippocampus. That’s noteworthy because the hippocampus is known for its involvement in remembering facts and events.
Unlocking the Brain’s Memory Retrieval System
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Credit:Sahay Lab, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
Play the first few bars of any widely known piece of music, be it The Star-Spangled Banner, Beethoven’s Fifth, or The Rolling Stones’ (I Can’t Get No) Satisfaction, and you’ll find that many folks can’t resist filling in the rest of the melody. That’s because the human brain thrives on completing familiar patterns. But, as we grow older, our pattern completion skills often become more error prone.
This image shows some of the neural wiring that controls pattern completion in the mammalian brain. Specifically, you’re looking at a cross-section of a mouse hippocampus that’s packed with dentate granule neurons and their signal-transmitting arms, called axons, (light green). Note how the axons’ short, finger-like projections, called filopodia (bright green), are interacting with a neuron (red) to form a “memory trace” network. Functioning much like an online search engine, memory traces use bits of incoming information, like the first few notes of a song, to locate and pull up more detailed information, like the complete song, from the brain’s repository of memories in the cerebral cortex.
New Evidence Suggests Aging Brains Continue to Make New Neurons
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins

Caption: Mammalian hippocampal tissue. Immunofluorescence microscopy showing neurons (blue) interacting with neural astrocytes (red) and oligodendrocytes (green).
Credit: Jonathan Cohen, Fields Lab, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, NIH
There’s been considerable debate about whether the human brain has the capacity to make new neurons into adulthood. Now, a recently published study offers some compelling new evidence that’s the case. In fact, the latest findings suggest that a healthy person in his or her seventies may have about as many young neurons in a portion of the brain essential for learning and memory as a teenager does.
As reported in the journal Cell Stem Cell, researchers examined the brains of healthy people, aged 14 to 79, and found similar numbers of young neurons throughout adulthood [1]. Those young neurons persisted in older brains that showed other signs of decline, including a reduced ability to produce new blood vessels and form new neural connections. The researchers also found a smaller reserve of quiescent, or inactive, neural stem cells in a brain area known to support cognitive-emotional resilience, the ability to cope with and bounce back from stressful circumstances.
While more study is clearly needed, the findings suggest healthy elderly people may have more cognitive reserve than is commonly believed. However, the findings may also help to explain why even perfectly healthy older people often find it difficult to face new challenges, such as travel or even shopping at a different grocery store, that wouldn’t have fazed them earlier in life.
Snapshots of Life: The Birth of New Neurons
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
After a challenging day at work or school, sometimes it may seem like you are down to your last brain cell. But have no fear—in actuality, the brains of humans and other mammals have the potential to produce new neurons throughout life. This remarkable ability is due to a specific type of cell—adult neural stem cells—so beautifully highlighted in this award-winning micrograph.
Here you see the nuclei (purple) and arm-like extensions (green) of neural stem cells, along with nuclei of other cells (blue), in brain tissue from a mature mouse. The sample was taken from the subgranular zone of the hippocampus, a region of the brain associated with learning and memory. This zone is also one of the few areas in the adult brain where stem cells are known to reside.
Snapshots of Life: Color Coding the Hippocampus
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
The final frontier? Trekkies would probably say it’s space, but mapping the brain—the most complicated biological structure in the known universe—is turning out to be an amazing adventure in its own right. Not only are researchers getting better at charting the brain’s densely packed and varied cellular topography, they are starting to identify the molecules that neurons use to connect into the distinct information-processing circuits that allow all walks of life to think and experience the world.
This image shows distinct neural connections in a cross section of a mouse’s hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in the memory of facts and events. The large, crescent-shaped area in green is hippocampal zone CA1. Its highly specialized neurons, called place cells, serve as the brain’s GPS system to track location. It appears green because these neurons express cadherin-10. This protein serves as a kind of molecular glue that likely imparts specific functional properties to this region. [1]
Cool Videos: Starring the Wiring Diagram of the Human Brain
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
The human brain contains distinct geographic regions that communicate throughout the day to process information, such as remembering a neighbor’s name or deciding which road to take to work. Key to such processing is a vast network of densely bundled nerve fibers called tracts. It’s estimated that there are thousands of these tracts, and, because the human brain is so tightly packed with cells, they often travel winding, contorted paths to form their critical connections. That situation has previously been difficult for researchers to image three-dimensional tracts in the brain of a living person.
That’s now changing with a new approach called tractography, which is shown with the 3D data visualization technique featured in this video. Here, researchers zoom in and visualize some of the neural connections detected with tractography that originate or terminate near the hippocampus, which is a region of the brain essential to learning and memory. If you’re wondering about what the various colors represent, they indicate a tract’s orientation within the brain: side to side is red, front to back is green, and top to bottom is blue.
Creative Minds: Helping More Kids Beat Anxiety Disorders
Posted on by Dr. Francis Collins
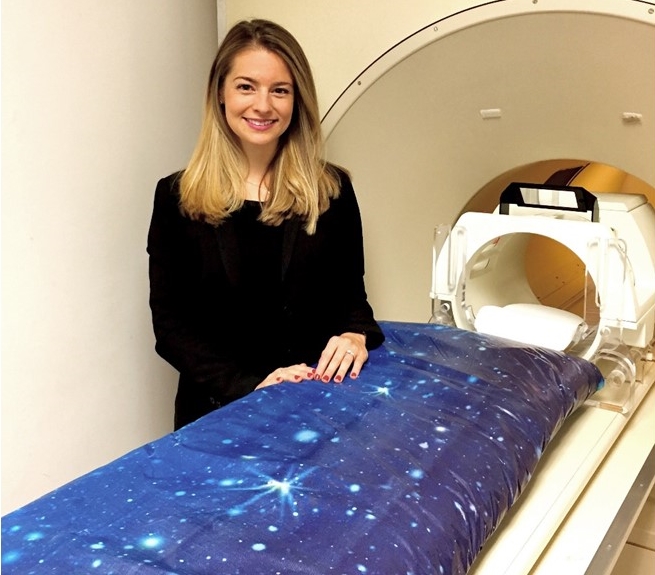
Dylan Gee
While earning her Ph.D. in clinical psychology, Dylan Gee often encountered children and adolescents battling phobias, panic attacks, and other anxiety disorders. Most overcame them with the help of psychotherapy. But not all of the kids did, and Gee spent many an hour brainstorming about how to help her tougher cases, often to find that nothing worked.
What Gee noticed was that so many of the interventions she pondered were based on studies in adults. Little was actually known about the dramatic changes that a child’s developing brain undergoes and their implications for coping under stress. Gee, an assistant professor at Yale University, New Haven, CT, decided to dedicate her research career to bridging the gap between basic neuroscience and clinical interventions to treat children and adolescents with persistent anxiety and stress-related disorders.
Previous Page Next Page



 For centuries, people have yearned for an elixir capable of restoring youth to their aging bodies and minds. It sounds like pure fantasy, but, in recent years, researchers have shown that the blood of young mice can exert a regenerative effect
For centuries, people have yearned for an elixir capable of restoring youth to their aging bodies and minds. It sounds like pure fantasy, but, in recent years, researchers have shown that the blood of young mice can exert a regenerative effect 
