 What is information blocking?
What is information blocking?
In general, information blocking is a practice by a health IT developer of certified health IT, health information network, health information exchange, or health care provider that, except as required by law or specified by the Secretary of Health and Human Services (HHS) as a reasonable and necessary activity, is likely to interfere with access, exchange, or use of electronic health information (EHI).
Have questions about information blocking? View our Information Blocking Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are examples of practices that could constitute information blocking?
Section 4004 of the Cures Act specifies certain practices that could constitute information blocking:
- Practices that restrict authorized access, exchange, or use under applicable state or federal law of such information for treatment and other permitted purposes under such applicable law, including transitions between certified health information technologies (health IT);
- Implementing health IT in nonstandard ways that are likely to substantially increase the complexity or burden of accessing, exchanging, or using EHI;
- Implementing health IT in ways that are likely to—
- Restrict the access, exchange, or use of EHI with respect to exporting complete information sets or in transitioning between health IT systems; or
- Lead to fraud, waste, or abuse, or impede innovations and advancements in health information access, exchange, and use, including care delivery enabled by health IT.
We provide many additional examples of practices that could constitute information blocking in ONC’s Cures Act Final Rule.
What are the information blocking exceptions?
Section 4004 of the Cures Act authorizes the Secretary of HHS to identify reasonable and necessary activities that do not constitute information blocking.
In the final rule, we have identified eight categories of reasonable and necessary activities (PDF - 555 KB) that do not constitute information blocking, provided certain conditions are met (referred to as “exceptions”). The exceptions support seamless and secure access, exchange, and use of EHI and offer actors (PDF - 243 KB)—health care providers, health IT developers, health information exchanges (HIEs) or networks (HINs)—certainty that practices that meet the conditions of an exception will not be considered information blocking.
A practice that does not meet the conditions of an exception would not automatically constitute information blocking. Such practices would not have guaranteed protection from civil monetary penalties or appropriate disincentives and would be evaluated on a case-by-case basis to determine whether information blocking has occurred.
The exceptions are divided into two classes:
- Exceptions that involve not fulfilling requests to access, exchange, or use EHI; and
- Exceptions that involve procedures for fulfilling requests to access, exchange, or use EHI.
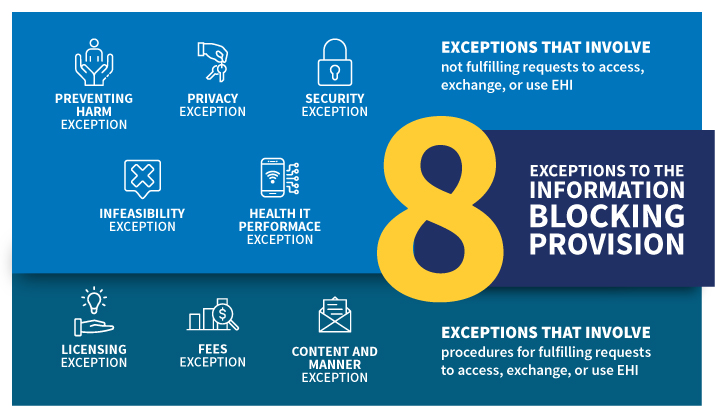
Exceptions that involve not fulfilling requests to access, exchange, or use EHI
Preventing Harm Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to engage in practices that are reasonable and necessary to prevent harm to a patient or another person, provided certain conditions are met.
Privacy Exception: It will not be information blocking if an actor does not fulfill a request to access, exchange, or use EHI in order to protect an individual’s privacy, provided certain conditions are met.
Security Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to interfere with the access, exchange, or use of EHI in order to protect the security of EHI, provided certain conditions are met.
Infeasibility Exception: It will not be information blocking if an actor does not fulfill a request to access, exchange, or use EHI due to the infeasibility of the request, provided certain conditions are met.
Health IT Performance Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to take reasonable and necessary measures to make health IT temporarily unavailable or to degrade the health IT's performance for the benefit of the overall performance of the health IT, provided certain conditions are met.
Exceptions that involve procedures for fulfilling requests to access, exchange, or use EHI
Content and Manner Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to limit the content of its response to a request to access, exchange, or use EHI or the manner in which it fulfills a request to access, exchange, or use EHI, provided certain conditions are met.
Fees Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to charge fees, including fees that result in a reasonable profit margin, for accessing, exchanging, or using EHI, provided certain conditions are met.
Licensing Exception: It will not be information blocking for an actor to license interoperability elements for EHI to be accessed, exchanged, or used, provided certain conditions are met.
How do I submit an information blocking complaint to ONC?
Information blocking complaints can be submitted through ONC’s online Health IT Feedback Form.
As specified by the Cures Act, information blocking claims and information received by ONC in connection with a claim or suggestion of information blocking are generally protected from disclosure under the Freedom of Information Act.

 Check ONC's LinkedIn Page
Check ONC's LinkedIn Page Follow ONC on Twitter
Follow ONC on Twitter Check ONC's YouTube Channel
Check ONC's YouTube Channel Subscribe/RSS
Subscribe/RSS
